As you may know, barley is rich in fiber and has a high nutritional value, including vitamins, minerals, and sugars. Recently, it has been attracting a lot of attention in Japan for its benefits in dieting, anti-aging, and beauty.
There are many types of barley, including rolled barley, MOCHI MUGI (glutinous barley), rolled barley, and rice barley. Also, they have its own unique appearance and texture. So there are many ways to enjoy them.
In addition, barley has an image of being healthy, but how does it actually compare to other grains? We will introduce its characteristics by comparing its sugars, energy, protein, and fiber, as well as its nutritional value.
“Sugar” don’t equal “carbohydrates.” Carbohydrates also contain dietary fiber.
In recent years, “carbohydrate restriction” has become popular as an effective method. When practicing carbohydrate restriction, many people may eliminate carbohydrates such as rice, bread, and noodles in addition to sweets. However, in fact, “sugars” don’t equal “carbohydrates.” “Sugar” is “carbohydrates” minus “fiber.”
In other words, carbohydrates contain not only sugars but also dietary fiber such as cellulose, which cannot be digested by the body. Therefore, even if the amount of carbohydrates is the same, if there is more dietary fiber, the amount of sugar will naturally be lower.
Sugars are our main source of energy. Completely eliminating them is not recommended.
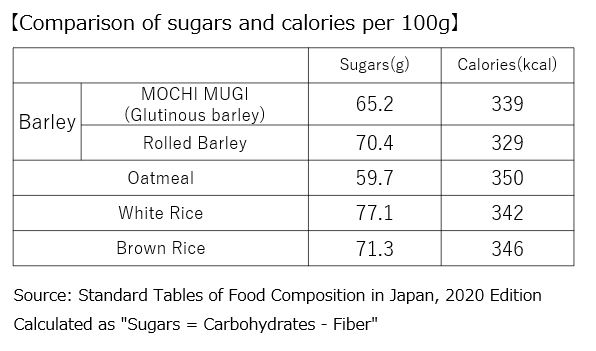
In this article, we will compare the sugar, energy, protein, and fiber of five types of grains: two types of barley (MOCHI MUGI and Rolled Barley), Oatmeal, White Rice, and Brown Rice.
First, comparing the sugars content per 100g, oatmeal has the lowest at 59.7g, followed by MOCHI MUGI at 65.2g. Also, compared to white rice, MOCHI MUGI has 15% less sugars and rolled barley has 10% less.
It is well known that excessive sugar should be avoided. However, sugars themselves are a source of energy for the body and brain and are essential for a health.
For example, a lack of sugars can lead to headaches, dizziness, fatigue, and etc. It isn’t recommended to completely eliminate sugars to lose weight.
Barley helps you feel full and reduces excessive calorie intake
Next, let’s look at energy. When comparing per 100g, there isn’t much difference. However, barley and oatmeal are more absorbent than white rice and other grains, so they keep you full longer.
They are also known to stimulate the satiety center and reduce hunger, ultimately preventing you from consuming too many calories. Also, be careful, as a lack of energy can lead to a loss of muscle mass, which makes it easier for the body to store fat.
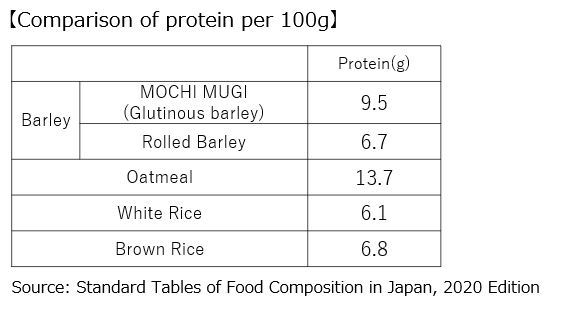
MOCHI MUGI has about 1.5 times the protein of white rice.
Protein, along with carbohydrates and lipids, is one of the three major nutrients and an important source of energy. It’s especially essential for building muscles, blood, and organs.
Comparing the protein content per 100g, oatmeal has the highest protein content at 13.7g, followed by MOCHI MUGI at 9.5g. Among barley varieties, MOCHI MUGI has more protein than rolled barley, about 1.5 times that of white rice and 1.4 times that of brown rice. Oatmeal also has about 2.2 times the protein of white rice and twice that of brown rice.
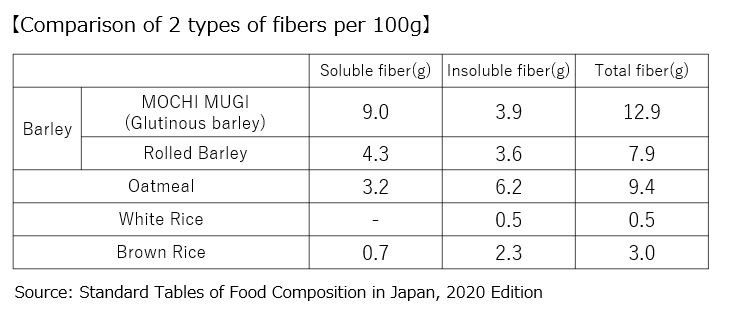
The soluble dietary fiber “β-glucan” has a weight-loss effect.
Barley is rich in water-soluble dietary fiber. Rolled barley has 4.3g per 100g, while MOCHI MUGI has 9.0g, far surpassing the others.
Particularly noteworthy is “β-glucan,” which accounts for over 70% of the water-soluble dietary fiber in barley. This “β-glucan” plays a role in lowering bad cholesterol in the blood, slowing the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates to prevent blood sugar levels from rising, and reducing visceral fat.
Barley is an ideal food source with a good balance of fiber and sugar
Barley has a good balance of carbohydrates, energy, and protein. Furthermore, its high dietary fiber content improves the intestinal environment, helping to alleviate constipation, a common pitfall in dieting.
Nowadays, it is popular not only in salads and soups, but also as a staple food in a variety of recipes. We hope you will incorporate barley into your diet and enjoy a healthy diet.

References
日本食品標準成分表2020年版(八訂):文部科学省 Standard Tables of Food Composition in Japan(2020 Edition)


